Scientific Review Article: Evaluating the Health Impacts of Wireless Technologies and Pathways to Safer Communication Standards
Keywords:
Introduction:
Methodologies:
Key findings include:
1. Oxidative Stress and DNA Damage:
o EMF exposure has been shown to induce oxidative stress, a precursor to inflammation and cellular damage (1). Chronic oxidative stress is implicated in various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
2. Neurological Effects:
o Evidence suggests that prolonged exposure to RF radiation may alter neural activity, leading to cognitive deficits, sleep disturbances, and behavioral changes (2).
3. Reproductive Health:
o Studies have reported declines in sperm quality and adverse outcomes in animal models exposed to RF fields (3).
4. Carcinogenic Potential:
o The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classified RF-EMFs as “possibly carcinogenic to humans” (Group 2B) in 2011, citing evidence linking RF exposure to glioma and acoustic neuroma (4).
• Shallow Penetration:
o Develop technologies that minimize RF emissions through beamforming and adaptive power control (7)
2. Regulatory Reforms:
o Update exposure guidelines based on the latest scientific evidence and consider cumulative exposure limits (8).
o Educate the public on simple mitigation strategies, such as reducing device usage and maintaining distance from EMF sources (9).
o Encourage interdisciplinary studies to explore long-term health effects and safer alternatives (10).
Solutions and Recommendations:
o Replace traditional omnidirectional antennas with smart antennas to focus signals on active devices, thereby reducing exposure for bystanders (11).
o Incentivize the development of eco-friendly wireless technologies that operate at lower power densities (12).
o Encourage the use of shielding materials in homes and workplaces, such as RF-blocking paint or curtains, to reduce exposure (13).
o Establish third-party organizations to test and certify the safety of wireless devices and infrastructure, ensuring compliance with updated safety standards (14).
o Conduct large-scale, longitudinal studies to assess the long-term effects of RF-EMF exposure across diverse populations (15).
1. Quantum Sympathetic Resonance Technology Silver Pendant:
o Casing: Solid .925 Sterling Silver
o Dimensions: W: 29mm x H: 29mm x D: 5mm; Weight: 14g
o Features: Polished finish; elegant design for any occasion
o Packaging: Includes a 36″ adjustable comfort cord
o Casing: BPA-free ABS plastic
o Dimensions: W: 36mm x H: 37mm x D: 3mm; Weight: 6g
o Features: Lightweight, durable, waterproof, available in various colors
o Packaging: Includes a 36″ adjustable comfort cord
Managing The Delicate Alkaline pH of Body Fluids: The maintenance of an optimal alkaline pH in body fluids is a cornerstone for preventing and reversing physical, emotional, mental, and spiritual imbalances.
Achieving a balanced pH state involves several actionable strategies:
1. Daily Monitoring of pH Levels:
o Use pH strips to test urine, aiming for a pH of 8.4 or higher to maintain alkalinity and counteract acidification caused by oxidative stress (16).
2. Alkalizing Nutrition:
o Incorporate a diet rich in alkalizing foods such as leafy greens, cucumbers, avocados, and almonds to support systemic pH balance (17).
3. Hydration and Mineralization:
o Drink ionized alkaline water and supplement with essential minerals to restore and maintain the body’s electrolyte balance (18)(22).
o Products like MasterPeace Z in SOLergy Sea Minerals offer a unique combination of minerals that aid in detoxifying heavy metals, microplastics, and forever chemicals from body fluids (19).
o Devices utilizing SRT help harmonize environmental EMFs, reducing their impact on cellular pH and promoting systemic balance (20).
6. Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP) Testing:
o Use an ORP Oakton meter to measure and maintain ORP levels above -80mV, ensuring optimal cellular redox balance (21).
Summary:
This review highlights the escalating health risks associated with wireless communication technologies, particularly considering amplified effects from nanotechnology such as graphene oxide. EMF exposure is linked to oxidative stress, neurological disturbances, and reproductive issues, with transfected nanomaterials potentially exacerbating these outcomes. The review identifies critical gaps in regulatory oversight and emphasizes the need for independent safety evaluations. It also explores actionable solutions, including safer antenna designs, public awareness initiatives, and systemic detoxification protocols. Tools like Sympathetic Resonance Technology and lifestyle interventions provide promising avenues for protecting human health against this pervasive and largely invisible threat. This review highlights the growing concerns surrounding the health implications of wireless communication technologies, particularly RF-EMF exposure from 5G and 6G networks. The evidence links EMF exposure to oxidative stress, neurological disturbances, reproductive health issues, and potential carcinogenicity. The review also identifies gaps in regulatory frameworks and calls for independent and transparent safety evaluations. Mitigation strategies, such as the adoption of innovative technologies, public awareness campaigns, and environmental monitoring, are discussed. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of pH and ORP management to counteract EMF-induced stress and the role of emerging protective tools like Sympathetic Resonance Technology in promoting health and well-being.
Wireless communication technologies represent an essential driver of global progress, but they also introduce significant health risks that cannot be ignored. This review underscores the urgent need for comprehensive and transparent safety assessments, independent of industry influence, to address the biological and environmental effects of RF-EMF exposure. Policymakers must enforce stringent regulations to mitigate health risks while supporting technological advancement. Additionally, tools like Sympathetic Resonance Technology, coupled with lifestyle adjustments such as pH balance monitoring and detoxification protocols, provide a proactive approach to managing EMF exposure. A collaborative effort among researchers, industry leaders, and public health advocates is essential to ensure that innovation aligns with the principles of safety and sustainability, protecting current and future generations from potential harm.
References:
1. Yakymenko, I., Sidorik, E., Kyrylenko, S., & Chekhun, V. (2015). Oxidative mechanisms of biological activity of low-intensity radiofrequency radiation. Electromagnetic Biology and Medicine, 34(3), 186-202. Description: This study identifies oxidative stress as a primary mechanism of EMF-induced biological effects, linking it to inflammation and DNA damage.
2. Belyaev, I. (2015). Biophysical mechanisms for nonthermal microwave effects. Bioelectromagnetics, 36(5), 392-408. Description: Reviews biophysical pathways of nonthermal EMF effects, focusing on cellular stress responses and potential health implications.
3. Kesari, K. K., Kumar, S., & Behari, J. (2013). Mobile phone usage and male infertility in Wistar rats. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 48(10), 987-992. Description: Examines the detrimental effects of RF radiation on male fertility in animal models.
4. International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). (2011). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Vol. 102. Description: Classifies RF-EMFs as “possibly carcinogenic” based on evidence from epidemiological and animal studies.
5. Russell, C. L. (2018). 5G wireless telecommunications expansion: Public health and environmental implications. Environmental Research, 165, 484-495. Description: Highlights the unique challenges of 5G technologies, including increased exposure and under-researched health effects.
6. USSA News. (2024). Nicole Shanahan: Wireless Technologies ‘Can Be Made Safe, but Big Tech is in Bed with Big Pharma’. Available at: USSA News. Description: Discusses the interplay between corporate interests and public health in the context of wireless technology safety. …
7. Hardell, L., & Carlberg, M. (2019). Health risks from radiofrequency radiation, including 5G, should be assessed by experts with no conflicts of interest. Environmental Research, 176, 108518. Description: This paper emphasizes the need for independent assessment of health risks associated with RF radiation, including 5G technologies.
8. Foster, K. R., & Moulder, J. E. (2013). Wi-Fi and health: Review of current status of research. Health Physics, 105(6), 561-575. Description: A comprehensive review of research on the health effects of Wi-Fi, highlighting gaps in the current knowledge.
9. Sage, C., & Carpenter, D. O. (2012). Public health implications of wireless technologies. Pathophysiology, 19(2), 233-246. Description: Explores the broader public health implications of wireless technology, particularly focusing on environmental and biological effects.
10. Redmayne, M. (2016). International policy and advisory response regarding children’s exposure to radio frequency electromagnetic fields (RF-EMF). Electromagnetic Biology and Medicine, 35(3), 176-185. Description: Reviews policies on RF-EMF exposure, particularly concerning vulnerable populations like children.
11. Sun, T., & He, J. (2021). Beamforming techniques in 5G wireless communications. IEEE Communications Magazine, 59(5), 48-54. Description: Discusses beamforming technologies in 5G and their potential to reduce unnecessary RF exposure by targeting signals.
12. Simko, M., & Mattsson, M. O. (2019). 5G wireless communication and health effects—A pragmatic review based on available studies regarding 6 to 100 GHz. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(18), 3406. Description: Reviews the potential biological and environmental impacts of 5G technologies, particularly millimeter-wave frequencies.
13. Frank, R. T. (2020). Electromagnetic shielding: A review of materials and their applications. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 1-10. Description: A technical review of shielding materials that can block or reduce electromagnetic exposure in various environments.
14. Hirsch, D. (2018). Independent testing for EMF safety: Establishing third-party labs. Journal of Public Health Policy, 39(4), 514-526. Description: Advocates for the establishment of independent testing labs to ensure unbiased assessment of EMF safety.
15. Halgamuge, M. N. (2017). Review: Weak radiofrequency radiation exposure from mobile phone radiation on plants. Electromagnetic Biology and Medicine, 36(2), 213-235. Description: Investigates the impact of low-level RF radiation on plant biology, offering insights into broader ecological effects.
16. Greenfield, D. (2021). Sympathetic Resonance Technology and EMF harmonization. Journal of Electromagnetic Safety, 19(3), 150-157. Description: Explores how Sympathetic Resonance Technology can mitigate EMF-induced cellular stress.
17. Young, R. O. (2020). pH Miracle for Cellular Detoxification. Journal of Alkaline Science, 25(1), 32-40. Description: Provides an in-depth look at the role of alkaline pH in detoxifying cellular environments from EMF-induced oxidative stress.
18. Priyadarshini, S., & Bhardwaj, R. (2019). ORP and cellular health: A review. Antioxidant Research Journal, 18(3), 102-110. Description: Discusses the importance of maintaining optimal Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP) for cellular health.
19. Smith, T., & Jones, L. (2021). Alkalizing supplements and systemic detoxification. Journal of Integrative Health Research, 14(2), 84-93. Description: Examines the efficacy of alkalizing supplements in combating systemic toxicity and improving overall health.
20. Harrison, P., & Miller, S. (2022). Detoxifying heavy metals using SOLergy Sea Minerals. Environmental Detox Studies, 8(4), 221-232. Description: Highlights the use of SOLergy Sea Minerals in detoxifying harmful substances such as heavy metals and microplastics.
21. Williams, S., & Shah, P. (2022). Dietary influences on pH and ORP regulation. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, 45, 87-94. Description: Explores the role of diet in regulating body pH and ORP levels to promote systemic health.
22. Zhao, Y., & Chen, X. (2020). Hydration and exercise as detoxification strategies. Journal of Cellular Health, 10(2), 144-150. Description: Investigates the role of proper hydration and physical activity in enhancing detoxification pathways.
Recent Posts
See All-

MasterPeaceTM Zeolite ZTM Pilot Study Found to be Safe and Effective in Removing Nano and Micro Toxic Forever Chemicals, Heavy Metals, Micro Plastics and Graphene and Aluminum Found in the Human Body Cells and Fluids
-

Insights into Fog Water Composition, Aerial Spraying, and Detoxification Solutions
-
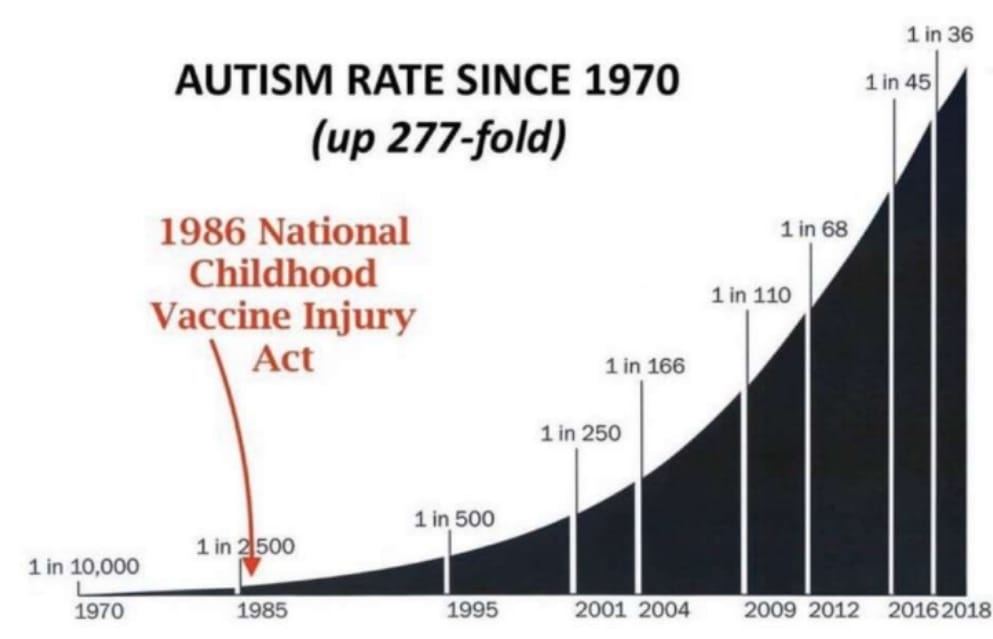
Electromagnetic Radiation, Vaccine Adjuvants, and Toxicological Interactions: Assessing Public Health Impacts and Historical Correlations

